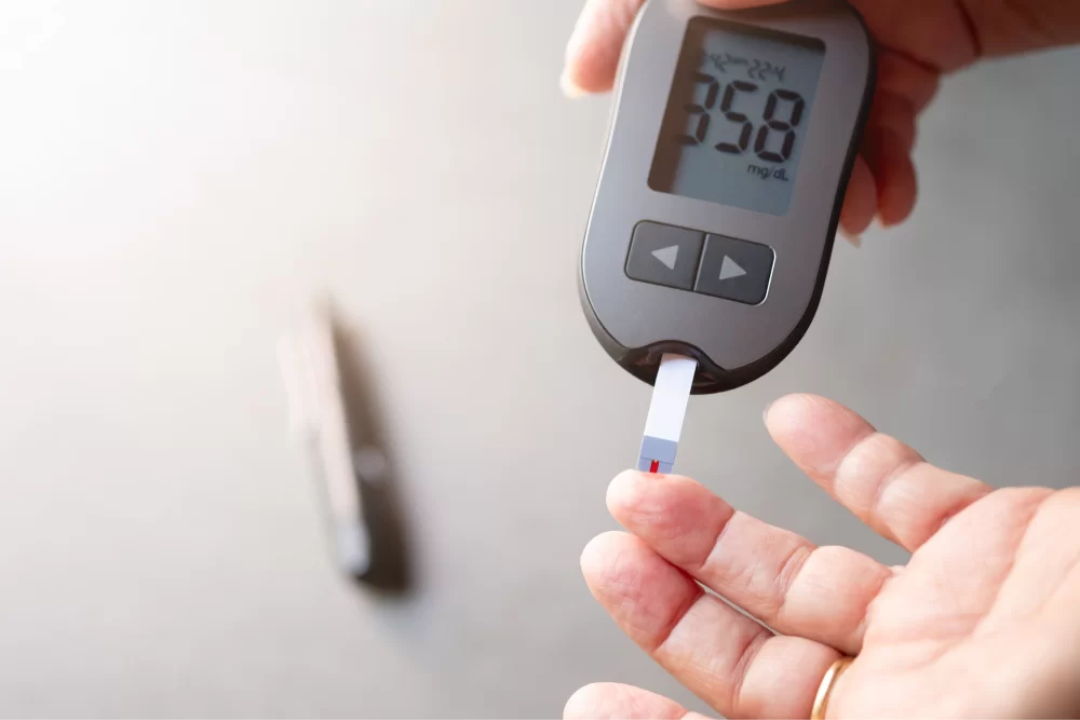
In the world of health, high blood sugar is a topic that goes far beyond simply overindulging in sweets. Check out how we can keep you informed:
In a context where chronic diseases are becoming increasingly prominent, understanding the origins of this increase in blood glucose is crucial to maintaining well-being.
Below, we detail the main causes of high blood sugar, exploring the different elements that can contribute to this condition and how this can directly impact our health and quality of life.
Be sure to follow this journey. Read on!
What is High Blood Glucose?
Glucose is a type of sugar found in the blood that provides energy to our body's cells.
When glucose levels are higher than normal, this is characterized as high glucose, also known as hyperglycemia.
Read also: Does a blood pressure app work? Discover 5 options!
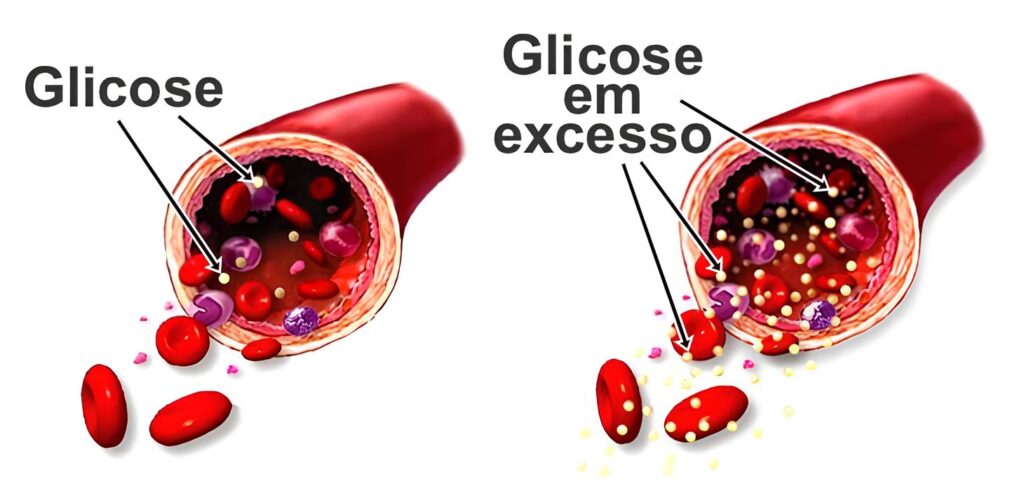
This can occur due to various factors, such as poor diet, lack of physical activity, insulin resistance or uncontrolled diabetes.
What are the Types of Diabetes?
When it comes to diabetes and pre-diabetes, it is essential to understand that there are several forms of this condition, each with its own specific characteristics and considerations.

5 Innovative Health Apps: the Road to Well-Being
You will be redirected to another website

5 Innovative Health Apps: the Road to Well-Being
Let's explore the main types:
1 - Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus:
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks the beta cells of the pancreas, which are responsible for producing insulin. This leads to a complete deficiency of insulin in the body.
Features:
- Need for daily insulin.
- It's not directly linked to lifestyle.
- Symptoms include thirst, frequent urination and weight loss.
- Risk of diabetic ketoacidosis.
- Diagnosed in children and young adults.
- Regular glucose monitoring is essential.
2 - Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus:
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes and is associated with insulin resistance and insufficient insulin production by the pancreas.
Features:
- Controlled by diet and exercise.
- Treatment can include oral medication or insulin.
- Risk factors include obesity and family history.
- It can be asymptomatic for a long time.
- Symptoms include thirst, frequent urination, fatigue and blurred vision.
- Higher incidence in adults and young people due to obesity.
3 - Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and usually disappears after childbirth.
Features:
- It develops during pregnancy due to insulin resistance.
- It can increase the risk for mother and baby.
- Controlled with diet and exercise, sometimes medication.
- Screening is part of prenatal care.
- Careful monitoring is essential.
4 - LADA type diabetes
LADA (Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults) is a rare form of diabetes that shares characteristics with type 1 and type 2.
Features:
- Onset in adults after the age of 30.
- Gradual autoimmune involvement.
- Slower progression than type 1.
- It may look like type 2, but it requires advanced insulin.
- Challenging diagnosis, requires medical follow-up.
5 - MODY type diabetes
MODY (Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young) is a hereditary form of diabetes that affects young people.
Features:
- Hereditary, onset before the age of 25.
- Caused by genetic mutations.
- It can be confused with other types.
- Responds well to oral medication.
- Diagnosis requires detailed genetic testing.
Symptoms and Causes of High Blood Glucose
Symptoms:
- Excessive thirst.
- Increased urinary frequency.
- Fatigue.
- Blurred vision.
- Unintentional weight loss.
Causes:
- A diet rich in sugars and carbohydrates.
- Lack of physical activity.
- Insulin resistance.
- Uncontrolled type 2 diabetes.
- Genetic and hereditary factors.
Risks Associated with Glucose
When glucose levels remain high for too long, our body faces a number of challenges that can significantly affect our health:

- Peripheral nerve damage: Imagine feeling tingling or pain in your hands and feet, something that can happen when the peripheral nerves are affected by high glucose.
- Renal complications: Our kidneys, which are the body's filters, can become overloaded and end up suffering damage, which can lead to serious kidney problems.
- Vision problems: Sight is a precious sense, but high glucose can damage our eyes, making them more susceptible to problems such as blurred vision and even loss of sight.
- Increased risk of cardiovascular disease: Our heart and blood vessels can be affected by high glucose, increasing the risk of diseases such as high blood pressure, heart disease and even strokes.
Looking after our glucose levels is more than a question of numbers; it's about ensuring a healthy, quality life.
Conclusion
As we can see, proper diabetes management and effective blood glucose control are key to ensuring good long-term health.
In this sense, technology has emerged as a valuable ally, offering innovative tools for the constant monitoring of blood glucose.
Therefore, whether through the use of modern technologies, regular exercise or a balanced diet, every step towards blood glucose control contributes significantly to a healthier and more balanced life.